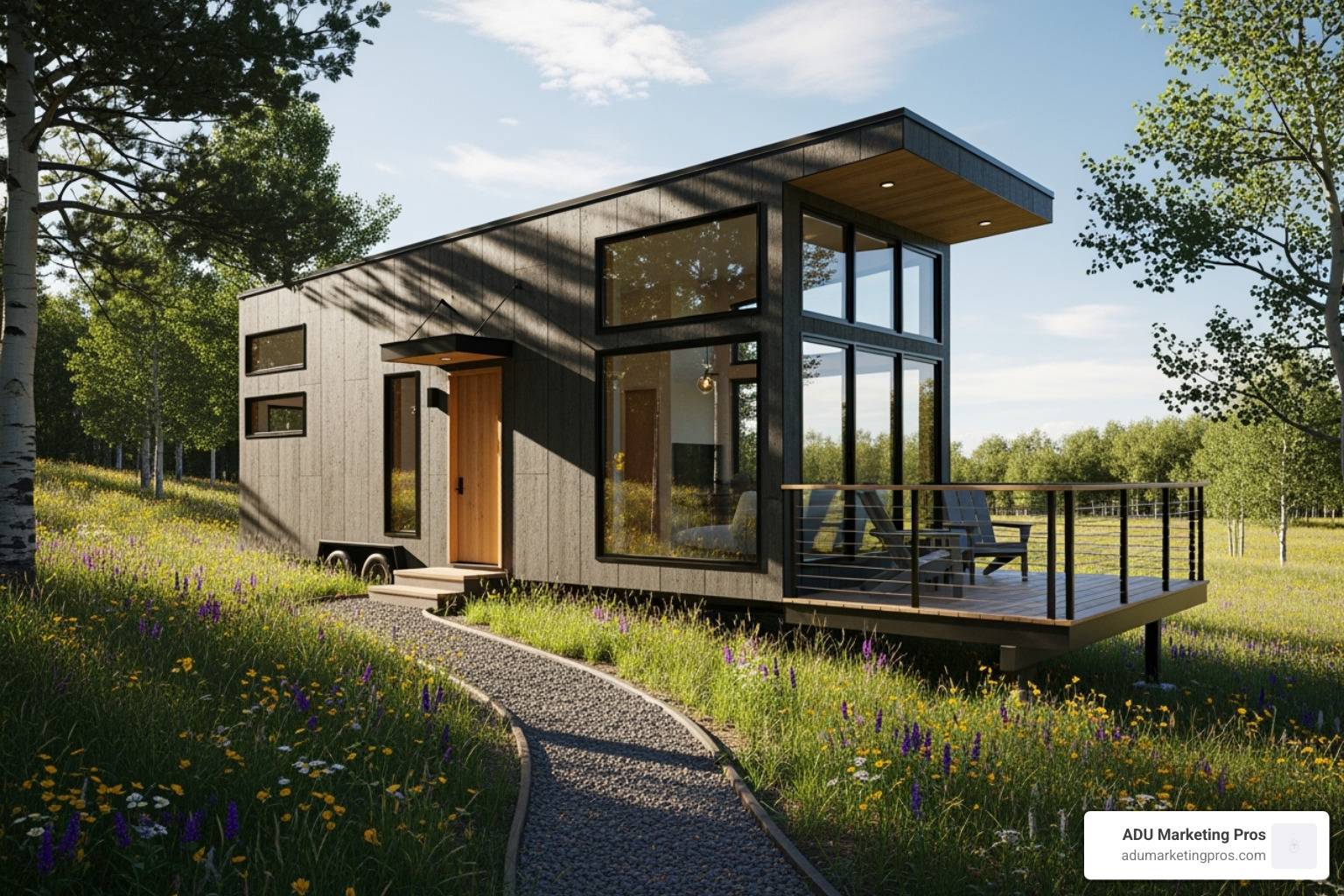
Why Prefab Tiny Homes Are Redefining Affordable Living
In the face of a relentless housing crisis, particularly in states like California where the dream of homeownership feels increasingly distant, a powerful solution is emerging: the prefab tiny home. These are not just downsized houses; they are intelligently designed, factory-built dwellings delivered to your property and installed in a fraction of the time of a traditional home. This innovative approach is reshaping the housing landscape, offering a viable path to affordable living and property expansion in markets demanding smarter, more efficient solutions.
A prefab tiny home is constructed off-site in a controlled factory setting, a process that ensures precision, quality, and speed. Once complete, the home is transported for final assembly on your land. This method directly confronts the primary obstacles of conventional construction: soaring costs, unpredictable timelines, and material waste.
Key facts about prefab tiny homes in California:
- Definition: A compact home constructed off-site in a factory, then transported to a property for final assembly and installation on a permanent foundation.
- Average California Cost: Approximately $135,060, which averages to about $393 per square foot. However, this can vary widely based on finishes, size, and site complexity.
- Build Time: A swift 3-6 months from start to finish, a stark contrast to the 9-12 months (or more) required for a traditional on-site build.
- Main Benefits: The advantages are clear: significantly faster construction, lower and more predictable costs, superior quality control due to the factory environment, and a more sustainable building process.
- Legal Status: Fully permitted as Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs) in California. State law mandates a 60-day review period for permits, drastically cutting down on bureaucratic delays.
The prefab movement is fundamentally about building smarter, not just smaller. By leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques in controlled environments, these homes offer consistent, high-quality construction with minimal material waste and zero weather-related setbacks. They present a compelling alternative for first-time homebuyers, those looking to downsize, and property owners seeking to add a rental unit or family guest house. For ADU builders, it’s a chance to expand their offerings in California’s dynamic and ever-evolving market.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through every aspect of the prefab tiny home journey, from understanding the different construction types and breaking down the true costs to navigating California’s permitting process and selecting the perfect builder to bring your vision to life.
What is a Prefab Tiny Home? Unpacking the Basics
Think of a prefab tiny home as a house built with the precision of modern manufacturing rather than the unpredictability of an open-air construction site. The term “prefab” is short for “prefabricated,” which simply means the home’s major components are built in a factory before being transported to your property for final assembly. This factory-based approach guarantees a level of quality, efficiency, and predictability that is nearly impossible to replicate with traditional on-site construction, which is often plagued by weather delays, inconsistent labor, and site-specific challenges.
While people often use “prefab” and “modular” interchangeably, it’s important to understand the distinction. Prefabrication is the broad, umbrella term for any type of off-site construction. Modular homes are a specific and very popular type of prefab. They are built as complete, three-dimensional sections, or “modules,” in a factory. These modules often arrive on-site 80-95% complete—with wiring, plumbing, flooring, and even fixtures already installed. They are then craned onto a permanent foundation and expertly joined together. In short, all modular homes are prefab, but not all prefab homes are modular.
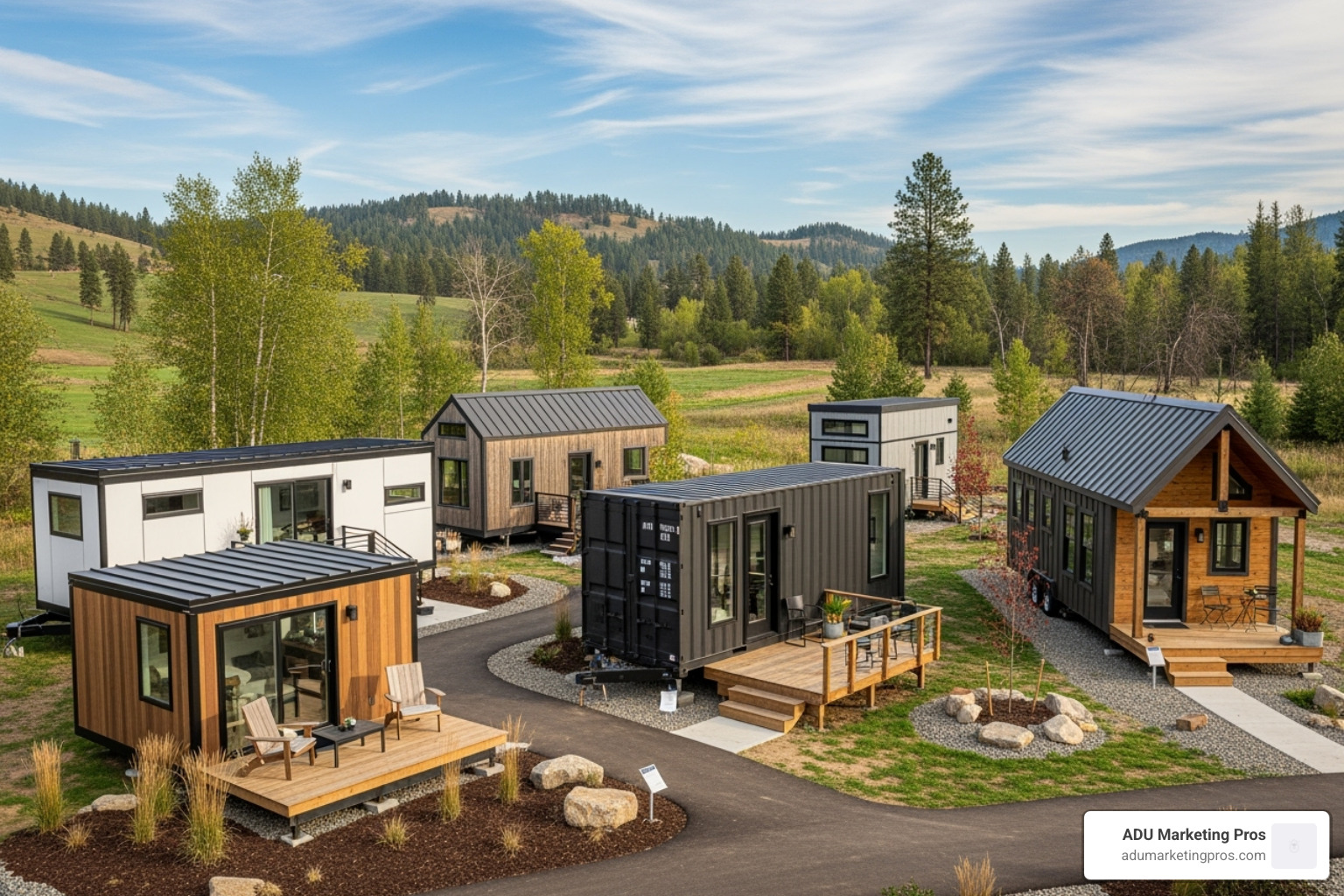

Main Types of Prefabricated Tiny Homes
The world of prefabrication is diverse, offering a range of construction methods to suit different budgets, timelines, and design preferences. Here are the most common types you’ll encounter:
- Modular Homes: As the most complete form of prefab, these homes are constructed as box-like modules that are connected on-site. This method offers the fastest installation time and results in a structure that is virtually indistinguishable from a site-built home, meeting the same stringent building codes.
- Panel-Built Homes (Panelized): In this method, the home’s structural components—walls, floors, and roof trusses—are built as flat panels in a factory. These panels are then shipped to the site and assembled like a large, high-quality puzzle. This approach allows for greater design flexibility and more architectural customization than modular construction, though it requires more on-site labor to finish.
- Kit Homes (Pre-Cut): A favorite among dedicated DIYers and those looking to manage their own build, kit homes include all the pre-cut and labeled materials needed for assembly. The homeowner or their contractor follows detailed instructions to construct the home on-site. Many modern kits feature advanced components like Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs), which are pre-insulated wall and roof sections that offer superior energy efficiency.
- Shipping Container Homes: A popular choice for their industrial-chic aesthetic and inherent durability, these homes repurpose steel shipping containers into modern living spaces. While visually striking, they require significant modification, including cutting openings for windows and doors, adding extensive insulation, and ensuring the metal is properly treated to create a comfortable and safe home.
- Foldable Homes: An innovative newcomer in the prefab space, these homes are engineered to fold flat for incredibly efficient transportation. Once on-site, they can be unfolded and installed in a matter of hours or days, making them an intriguing option for rapid housing deployment or accessory units.
- Tiny Homes on Wheels (THOWs): While many THOWs are factory-built, they occupy a different legal category. Because they are on a chassis, they are typically classified and registered as recreational vehicles (RVs). This distinction is critical, as it heavily influences where they can be legally placed and whether they can be used as a permanent residence, which is often restricted by local zoning laws.
The Prefab Advantage: Why Choose Factory-Built Over Traditional Construction?
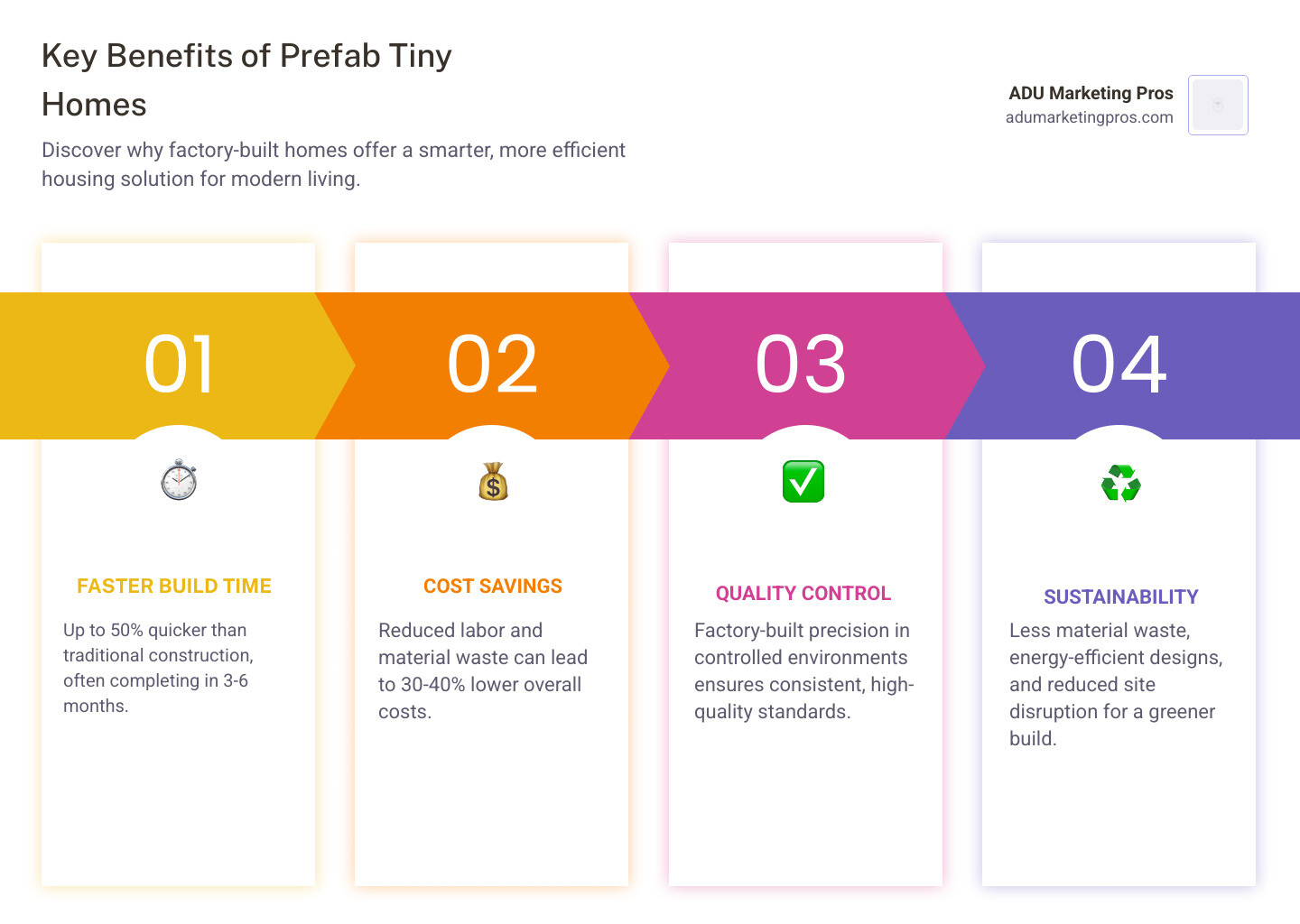
Opting for a prefab tiny home is more than a style choice; it’s a strategic decision that delivers measurable advantages in speed, cost, quality, and sustainability when compared to traditional on-site construction. The factory-controlled process eliminates many of the variables that make conventional building projects stressful and expensive.
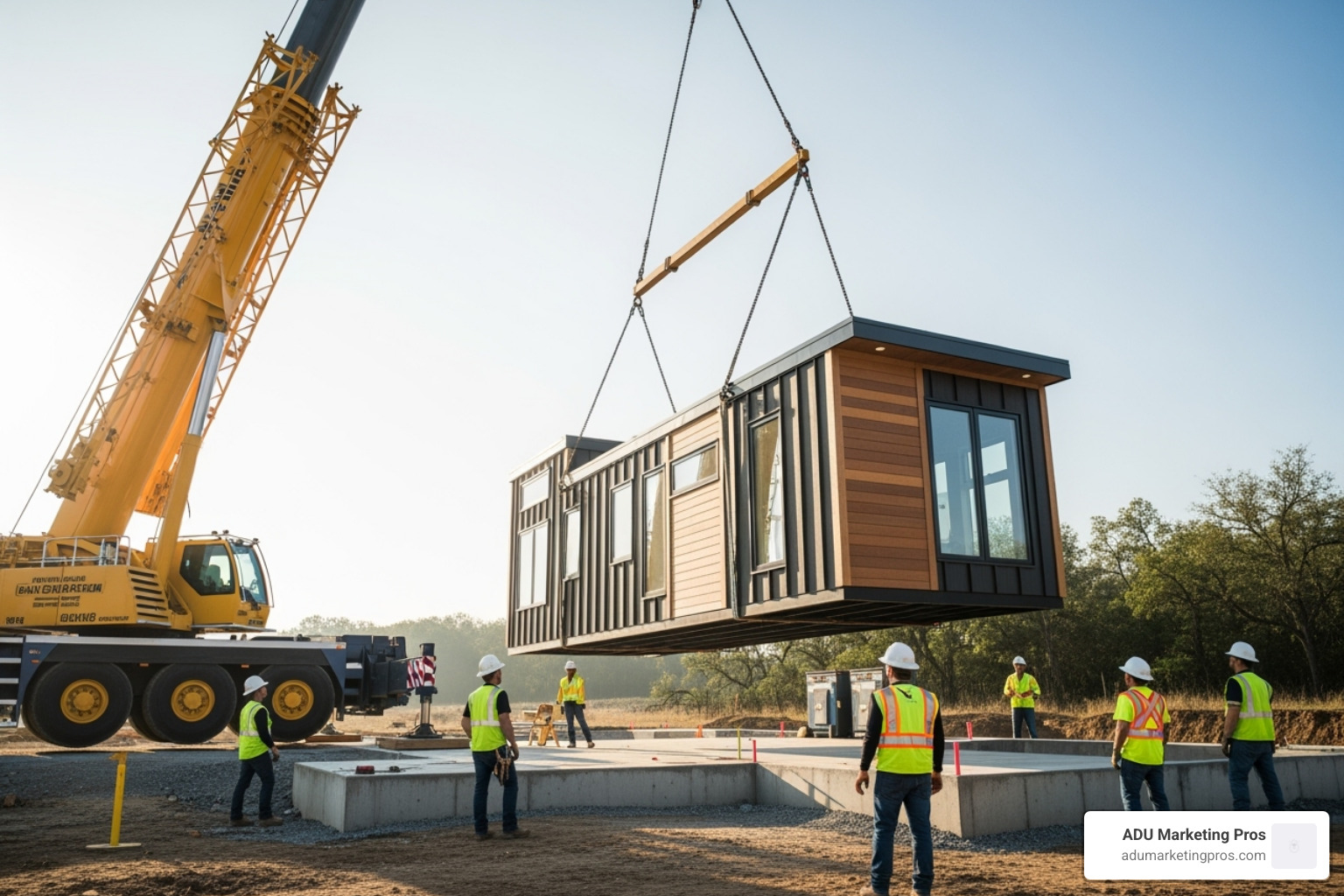

First and foremost is speed. A prefab home is manufactured in a factory at the same time your property’s foundation and utilities are being prepared. This parallel workflow, known as simultaneous construction, is the key to cutting the typical building timeline in half. You can often move into your new home in months, not years. Second, there’s cost-effectiveness. Prefab manufacturers purchase materials in bulk, reducing costs. Precision equipment and automated processes minimize material waste, and an efficient factory workforce reduces labor hours. This translates into a more predictable, fixed budget, shielding you from the surprise expenses and cost overruns common in traditional projects.
Prefab construction also means minimal site disruption. The majority of the construction activity—the noise, dust, and traffic—is confined to the factory. This keeps your property cleaner and your neighbors happier. From an environmental perspective, prefab is a clear winner. The controlled setting allows for meticulous material management and waste reduction, with many factories recycling up to 80-90% of their waste. Furthermore, many builders prioritize sustainable materials, such as reclaimed wood, bamboo, and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) paints. The precision build also creates a tighter building envelope, significantly improving energy efficiency. Some prefab homes are even built to meet rigorous green building standards like those set by the U.S. Green Building Council’s LEED program.
Cost and Build Time Comparison
The differences between prefab and traditional construction become undeniable when you compare them side-by-side:
| Metric | Prefab Tiny Home | Traditional On-Site Build |
|---|---|---|
| Average Build Time | 3-6 months | 9-12+ months |
| Cost Predictability | High (Fixed factory pricing) | Variable (Subject to market fluctuations, labor shortages) |
| Material Waste | Very Low (Optimized, recycled) | High (10-15% of materials can be wasted) |
| Quality Control | High (Multi-point factory inspections) | Variable (Dependent on individual contractor skill) |
| Weather Delays | None (Indoor construction) | Frequent (Rain, wind, and cold can halt progress) |
| Site Disruption | Minimal (Weeks of on-site work) | Extensive (Months of noise, dust, and traffic) |
Sustainability and Quality Control
The factory environment is the cornerstone of the prefab advantage. Protected from the elements, workers can use advanced tools and machinery to ensure every cut is perfect and every joint is secure. This results in a structurally superior and more airtight building, which directly translates to better energy efficiency, lower utility bills, and long-term durability.
Quality is not an afterthought; it’s a continuous process. Homes on a factory line undergo rigorous, multi-stage inspections—from framing and electrical to plumbing and finishes—by dedicated quality control managers. This level of oversight is nearly impossible to achieve on a traditional job site, where inspections are intermittent. This consistent quality, combined with sustainable building practices, makes prefab a smarter, more responsible, and ultimately more reliable way to build.
The Cost of Living Small: A California Prefab Tiny Home Price Guide
In California’s notoriously expensive housing market, prefab tiny homes present a genuinely accessible path to homeownership or property enhancement. However, creating a realistic budget requires a clear understanding of all the costs involved—from the factory price to the final handshake with your contractor.

Average Costs and What They Include
The average cost for a turnkey prefab tiny home in California hovers around $135,060, which breaks down to about $393 per square foot. This is a useful benchmark, but the actual price can range from as low as $77 per square foot for a basic kit home to over $940 per square foot for a highly customized, high-end modular unit.
It is absolutely critical to clarify what a builder’s quoted price includes. A “base price” might only cover the structural shell of the home delivered to your curb. A “turnkey” price, on the other hand, should ideally cover everything needed to make the home move-in ready: interior and exterior finishes, appliances, delivery, installation, and utility connections. Always request a detailed line-item proposal to see exactly what you’re paying for.
Factors That Influence the Final Price
Your total project cost will be a sum of the home’s factory price plus several site-specific expenses. These “soft costs” can typically add $30 to $60 per square foot, or more for complex sites.
- Size and Layout: Larger homes with more complex designs cost more to build and transport.
- Customization and Finishes: Upgrading from standard vinyl flooring to hardwood, or from laminate countertops to quartz, will increase the price. Custom cabinetry, high-end appliances, and unique architectural features also add to the cost.
- Foundation Type: A simple concrete slab on a flat lot is the most affordable option. A raised perimeter or pier-and-beam foundation, often required for sloped lots, will cost more.
- Site Preparation: This is a major variable. A flat, easily accessible lot will be far cheaper to prepare than a sloped, rocky, or remote property that requires significant grading, excavation, tree removal, or a long driveway.
- Transportation and Installation: These fees cover the specialized truck to transport the home modules and the crane required to lift them onto the foundation. Costs increase with distance from the factory and difficulty of site access.
- Permits and Utility Hookups: Budget for local planning and building permit fees, which can run into thousands of dollars. You’ll also need to pay licensed contractors to connect the home to water, sewer/septic, and electrical grids. Some cities also charge “impact fees” to cover the new unit’s demand on public services.
Financing Your Prefab Tiny Home
Securing a loan for a prefab ADU is becoming easier, but it differs from a traditional mortgage. Since the home is built before it’s attached to the property, a standard mortgage isn’t an option. Instead, homeowners typically use:
- Construction-to-Permanent Loans: These two-part loans provide short-term funds to the factory during construction, then convert to a long-term mortgage once the home is installed.
- Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) or Home Equity Loan: If you have sufficient equity in your primary residence, you can borrow against it to finance the ADU.
- Cash-Out Refinance: This involves refinancing your existing mortgage for a higher amount and using the difference to pay for the project.
- Personal Loans: For smaller or lower-cost projects, an unsecured personal loan can be a viable, albeit higher-interest, option.
Many prefab builders have relationships with lenders who specialize in ADU financing and can guide you through the process. Resources like the California Housing Finance Agency (CalHFA) also offer grant and loan programs to help homeowners finance their ADUs.
From Blueprint to Backyard: Navigating the Legal and Building Process in California
Building a prefab tiny home on your California property is more feasible than ever, thanks to progressive state legislation designed to combat the housing shortage. However, the process still requires careful planning and a clear understanding of both state and local regulations to ensure a smooth journey from design to occupancy.

Key Legal Requirements for a Prefab Tiny Home
In California, a prefab tiny home installed on a permanent foundation is legally classified as an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU). A series of state laws, including AB 68 and SB 9, have streamlined the approval process and removed many common barriers:
- 60-Day Approval Timeline: By law, municipalities must approve or deny a completed ADU permit application within 60 days. This prevents applications from languishing in planning departments for months on end.
- Elimination of Barriers: State law has largely eliminated owner-occupancy requirements, minimum lot size restrictions, and off-street parking requirements for ADUs located near public transit or in historic districts.
- Pre-Approved ADU Programs: To further expedite permitting, many cities like San Jose and Los Angeles offer pre-approved ADU plans. If you choose one of these designs, your permit can often be issued much faster, sometimes even over the counter.
While state law sets the minimum standards, you must still comply with local zoning ordinances. These local rules will dictate specifics like maximum unit size, height limits, and setback distances from property lines. Working with a builder or architect who is an expert in your specific city’s codes is crucial for a successful project.
The Step-by-Step Building and Permitting Process
- Feasibility and Design: The first step is to work with your builder to determine what is possible on your property. This includes a site analysis and selecting or designing a home that meets your needs and local codes.
- Plan Submission: Your builder or architect will create a full set of construction documents and submit them to your local planning and building department.
- Plan Check and Revisions: City officials will review the plans for compliance with all building, safety, and zoning codes. They may return the plans with comments or required corrections.
- Permit Issuance: Once all corrections are made and plans are approved, the city will issue the building permit. At this point, factory construction and site preparation can begin in earnest.
- Construction and Inspections: While the home is built in the factory, your on-site contractor will prepare the foundation and utilities. Both the factory work and the site work will undergo inspections.
- Delivery and Installation: The completed home modules are transported to your property, craned into place, and secured.
- Final Hookups and Inspection: The final utility connections are made, and a final inspection is performed by the city. Once passed, you receive a Certificate of Occupancy and can move in.
How to Choose the Right Builder
Your builder is your most important partner in this process. A great builder simplifies the complexities of permitting, manages timelines, and delivers a high-quality product.
- Verify Credentials: Check their contractor’s license on the California State License Board (CSLB) website. Ensure they have adequate insurance. For THOWs, RVIA certification is a non-negotiable mark of safety and quality.
- Review Their Portfolio and References: Scrutinize photos of their past work. More importantly, ask for a list of past clients and call them. Ask about their experience with communication, budget adherence, and the final quality of the home.
- Understand the Contract: A detailed contract is your best protection. It should clearly outline the full scope of work, a payment schedule, material specifications, a project timeline, and a warranty. Read it carefully and ask questions.
- Prioritize Communication: Choose a builder who is responsive, transparent, and proactive. You should feel comfortable with their communication style and confident they will keep you informed throughout the project.
Designing Your Dream: Features, Customization, and Long-Term Living
One of the most exciting aspects of getting a prefab tiny home is the opportunity to design a space that is a perfect reflection of your lifestyle. It’s a masterclass in efficiency and personalization, where every square inch is thoughtfully planned to create a home that is as beautiful as it is functional.
Popular Features and Customization Options
Modern prefab tiny homes can be equipped with a vast array of features to maximize comfort, utility, and style. You are not limited to a one-size-fits-all design.
- Multi-functional Furniture: This is the cornerstone of smart small-space design. Think Murphy beds that vanish into the wall to reveal a desk or sofa, dining tables that fold away, and benches that offer hidden storage.
- Lofted Bedrooms: Lofts are a classic tiny home feature, creating a cozy, separate sleeping area that doesn’t consume valuable floor space. This keeps the main level open for living, cooking, and dining.
- Full-Size Kitchens and Baths: Forget the cramped kitchens of old RVs. Many modern prefab designs accommodate full-size appliances, generous counter space, and comfortable, well-appointed bathrooms with walk-in showers and standard toilets.
- Smart Home Technology: Integrate modern convenience with systems for lighting, climate control (like a Nest thermostat), security cameras, and smart locks, all controllable from your smartphone.
- Off-Grid Capabilities: For ultimate sustainability and independence, you can equip your home with a full solar panel and battery storage system, rainwater harvesting and filtration systems, and composting toilets to minimize your reliance on public utilities.
- Indoor-Outdoor Living: Large windows, panoramic sliding glass doors, and attached decks or patios are crucial for making a small space feel larger. They blur the line between inside and out, connecting you to nature and expanding your usable living area.
- Personalized Finishes: This is where you make the home truly yours. Most builders offer a wide selection of exterior siding, interior paint colors, flooring materials (from LVP to hardwood), countertop styles (laminate, butcher block, quartz), and hardware finishes.
Layout and Floor Plan Strategies
A successful tiny home design hinges on its floor plan. When working with your builder, consider these strategies:
- Prioritize Natural Light: Use large, strategically placed windows and glass doors to flood the space with light, making it feel more open and airy. Clerestory windows can add light while maintaining privacy.
- Create Zones: Even in an open-plan layout, you can use furniture, rugs, or subtle architectural cues to define different zones for living, dining, and working. This creates a sense of order and purpose.
- Go Vertical with Storage: Take advantage of the home’s full height. Use tall, built-in shelving, overhead cabinets, and lofted storage areas to keep clutter off the floor.
- Consider Accessibility: If you plan to age in place, consider a single-story layout, a main-floor bedroom, a curbless walk-in shower, and wider doorways to ensure long-term comfort and safety.
The Long-Term Reality of a Prefab Tiny Home
Living in a tiny home is a distinct lifestyle choice with profound benefits and some practical challenges.
The Benefits:
- Financial Freedom: A significantly lower initial investment and drastically reduced monthly expenses (utilities, taxes, maintenance) can free up immense financial resources, allowing you to pay off debt, save, or invest.
- Simplified Lifestyle: With less space to clean and fewer possessions to manage, you gain back valuable time and mental energy to focus on hobbies, travel, relationships, and experiences.
- Lower Environmental Impact: A smaller home consumes fewer resources to build and operate, resulting in a much smaller carbon footprint over its lifetime.
The Challenges:
- Limited Space: This is the most obvious trade-off. It requires a conscious commitment to minimalism and can be challenging for large families, avid collectors, or those who frequently host large gatherings.
- Resale Value: The market for tiny homes is growing but remains a niche. A prefab ADU on a permanent foundation will appreciate in value along with the property, making it a solid investment. A Tiny Home on Wheels (THOW), being personal property like an RV, will depreciate over time.
- Social Perceptions: While gaining acceptance, you may still encounter questions or skepticism from friends, family, or even financial institutions unfamiliar with the value and legitimacy of well-built, permanently sited tiny homes.
Frequently Asked Questions about Prefab Tiny Homes
Navigating the world of prefab tiny homes can bring up a lot of questions. Here are answers to some of the most common inquiries.
How do prefab and modular homes differ?
“Prefabricated” (prefab) is the all-encompassing term for any home with components built in a factory. Modular homes are a specific type of prefab. They are built as complete, three-dimensional sections, or “modules,” in a factory. Other prefab types include panel-built homes (2D panels assembled on-site) and kit homes (pre-cut materials for DIY assembly). So, while all modular homes are a form of prefab, not all prefab homes are modular.
Is it cheaper to build on-site or buy a tiny prefab home?
In the vast majority of cases, a prefab tiny home is more affordable. The efficiencies of factory construction—bulk material purchasing, reduced labor hours, and minimal waste—lead to significant cost savings. While you must still budget for site work, foundation, delivery, and installation (which can add $30-$60 per square foot or more), the total project cost is typically lower and, crucially, more predictable than a traditional on-site build, which is prone to cost overruns.
How long does it really take to build a prefab tiny home?
The typical timeline from signing a contract to moving in is 3-6 months. This remarkable speed is achieved through simultaneous construction: the home is built in the factory while the foundation and site utilities are prepared at the same time. The final on-site installation is very fast, often taking just a few days to a week. The biggest variable that can extend this timeline is the local permitting process, although California’s 60-day mandatory review period helps to expedite this stage significantly.
Can I put a prefab tiny home anywhere in California?
No. For a permanent residence, a prefab tiny home must be installed on a foundation on a properly zoned residential lot and is typically permitted as an Accessory Dwelling Unit (ADU). You must follow all local zoning rules regarding setbacks, size, and height. Tiny Homes on Wheels (THOWs) are classified as RVs and face much stricter placement rules; they are generally not legal as full-time residences in backyards, except in a few specific cities with progressive ordinances.
How are prefab tiny homes financed?
Traditional mortgages are not used for prefab construction because the home isn’t yet real estate. Instead, common financing methods include construction-to-permanent loans, home equity loans or lines of credit (HELOCs), cash-out refinancing of your primary mortgage, or personal loans. Many prefab companies have partnerships with lenders who specialize in these types of loans and can help you navigate the process.
Are prefab tiny homes energy-efficient?
Yes, they are typically more energy-efficient than traditionally built homes. The precision of factory construction creates a much tighter building envelope, reducing air leakage. Builders often use advanced insulation products like Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs) and high-performance windows. These factors combine to lower heating and cooling costs and create a more comfortable living environment.
Conclusion: Is a Prefab Tiny Home Your Path to Smarter Living?
Prefab tiny homes represent a fundamental and exciting shift in our approach to housing. With build times as short as 3-6 months, significant and predictable cost savings, and a level of quality control that site-building can’t match, they offer a powerful and tangible solution to California’s housing affordability crisis. These homes are not just about shrinking your living space; they are about expanding your life by embracing a more intentional, sustainable, and financially secure lifestyle.
While the minimalist nature of tiny living requires thoughtful planning and a shift in mindset, the rewards are immense. Lower utility bills, reduced maintenance burdens, and a smaller environmental footprint are compelling advantages that resonate with a growing number of homeowners. Thanks to California’s forward-thinking ADU regulations, this path to homeownership or property enhancement is more accessible than ever before.
Making an informed decision begins with finding the right professional partners who can guide you through the process. At ADU Marketing Pros, we specialize in connecting homeowners with the top ADU construction and architecture firms in California. We understand the nuances of the local market and can help you find the certified experts who will turn your vision for a prefab tiny home into a beautiful reality.
If you’re ready to explore how a smarter, more efficient home can fit into your life, the next step is to consult with the experts. Find expert tiny house builders in California to start your project and take the first step on a smarter path to living.





